Sentinel chicken surveillance reveals previously undetected circulation of West Nile virus in the Netherlands
This publication is part of the project ‘Preparing for vector-borne virus outbreaks in a changing world: a One Health Approach’ (NWA.1160.1S.210) which is (partly) financed by the Dutch Research Council (NWO).
Authors: Kiki Streng, Nnomzie Atama, Felicity Chandler, Rody Blom, Henk van der Jeugd, Maarten Schrama, Marion P.G. Koopmans, Wim H.M. van der Poel & Reina S. Sikkema
ABSTRACT
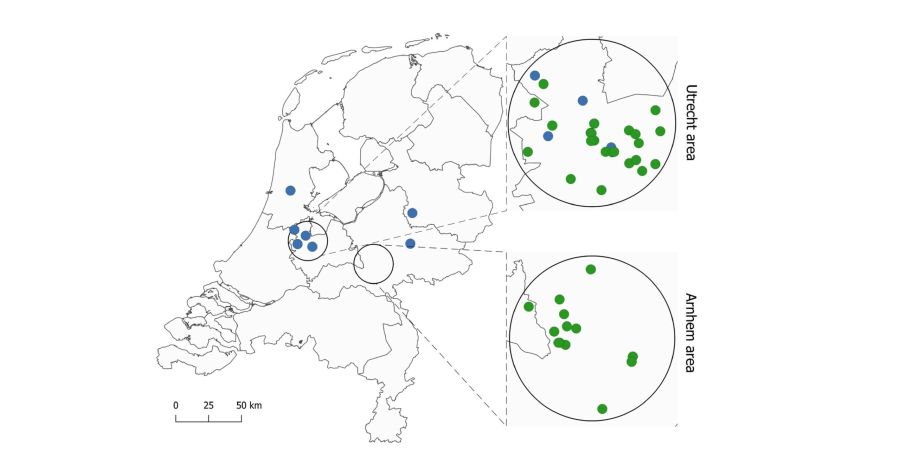
West Nile virus (WNV) was first detected in the Netherlands in 2020, with circulation observed in birds, mosquitoes, and humans in two geographical areas. Usutu virus (USUV) has been circulating in the Netherlands since 2016. Following the detection of WNV in the Netherlands, we investigated the possible use of petting zoos as urban sentinel sites to examine the extent of WNV and USUV circulation around the two WNV outbreak locations. Chickens at petting zoos and in backyards were sampled within a 15-kilometer radius of the confirmed WNV circulation areas at three timepoints over one year (2021–2022). Sera were analysed using a protein microarray for binding antibodies to orthoflavivirus NS1 antigens and reactive samples were confirmed through micro-focus reduction neutralization tests (mFRNT). Furthermore, mosquitoes at sampling locations were collected to assess their blood feeding behaviour. This serosurvey detected the circulation of USUV and WNV in petting zoo and backyard chickens in 2021, both within and outside the 2020 outbreak areas. The WNV circulation was not detected by other existing surveillance schemes in mosquitoes, wild birds, horses and humans. In addition, the results show rapid decay of USUV antibodies in approximately 20 weeks. Our findings support the utility and the added value of petting zoo chickens as sentinels for monitoring USUV and WNV circulation compared to other available methods. Seroconversions observed in petting zoos and backyard chickens living in or near densely populated urban areas further highlighted potential public health risks that went undetected.
Read the whole publication here.
Source: Taylor & Francis online: Emerging Microbes and Infections